
10
Chapter 1: Introduction and Graphical Displays
Definition: Statistic
A statistic is a characteristic or a fact about a sample.
For example, we may be interested in studying the distribution of the heights
of National Basketball Association (NBA) players. If the average height of
a sample of listed players is 6.37 feet, then this will be the value of the
sample average.
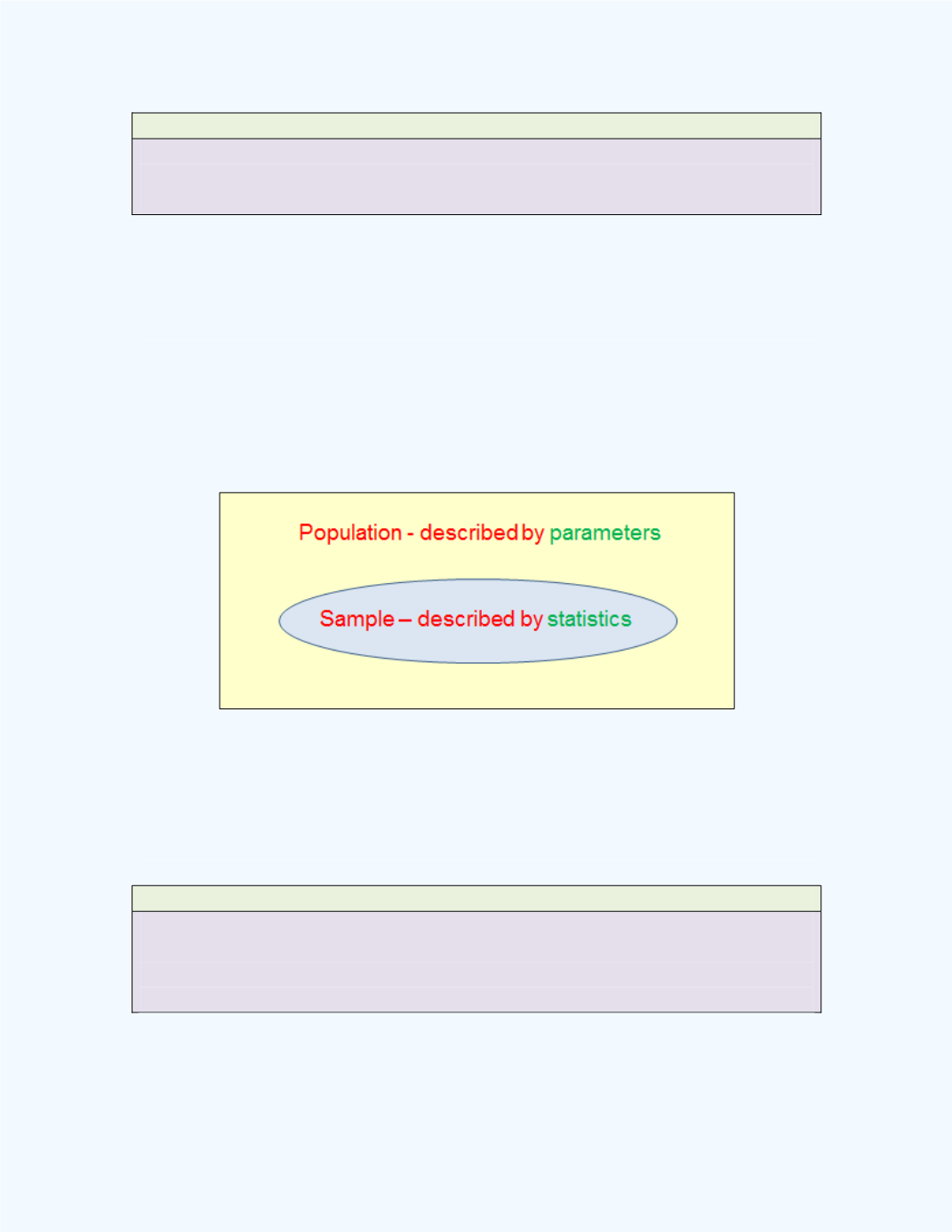
Since parameters are descriptions of the population, a population can have
many parameters. Similarly, a sample can have many statistics. We will
encounter several parameters and statistics in subsequent chapters of this
e-book. These associations are shown in
Figure 1-4
.
Figure 1-4:
The difference between parameters and statistics
When selecting a sample, researchers would like to select values in such a
way that there is no inherent bias. One way of doing this is by selecting a
random sample
.
Definition: Random Sample
A random sample is one in which every member of a population has an
equal chance of being selected at every stage of the sampling process.
Note:
If the sample sizes are equal, we refer to this random sample as a
simple random sample.
















