
8
Chapter 1: Introduction and Graphical Displays
One of the main responsibilities of a statistician is to analyze data. Hence,
one of the first functions will be to collect data. One of the things
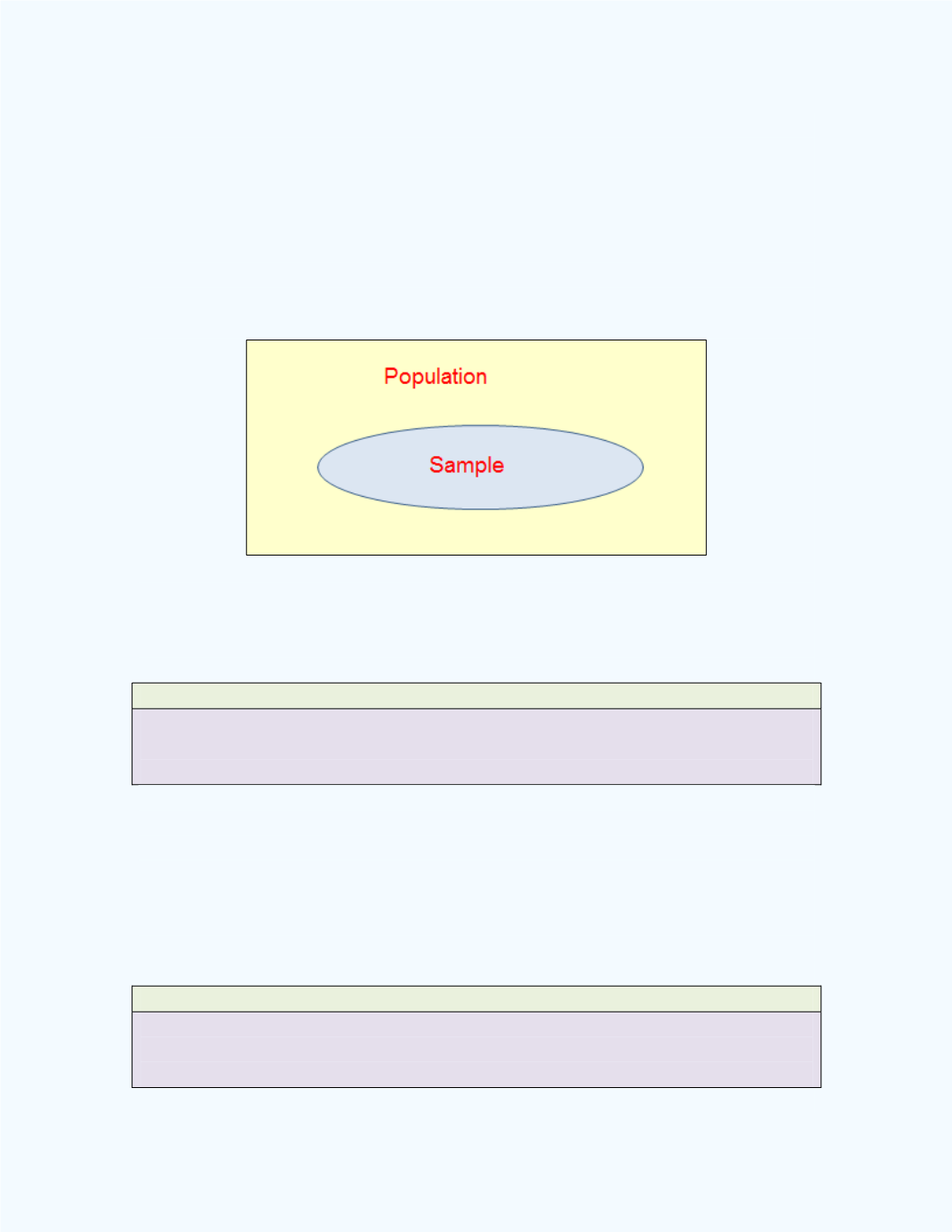
statisticians may want to do is to make some inference on or make a general
statement about a characteristic of an entire group or a
population
. For a
great deal of situations, it is impractical or too expensive to collect data from
the entire population. In such instances, the statistician may select a
representative portion of the population, called a
sample
. This is depicted in
Figure 1-3
.
Figure 1-3:
The relationship between a sample and a population
The definition of a population is given next.
Definition: Population
A population consists of all subjects which are being studied.
For example, we may be interested in studying the distribution of the ACT
math scores for four year college students in the state of Kentucky. In this
case, the population will be the ACT math scores for
all
the students
enrolled in four year colleges in the state of Kentucky.
Following is a definition of a sample.
Definition: Sample
A sample is a subset of the population.
















