
Chapter 7: Probability
297
Notation:
We will let
P
(
A
|
B
) represent the conditional probability of the
event
A
given that event
B
has occurred. It is read as “the probability of
A
given
B
”.
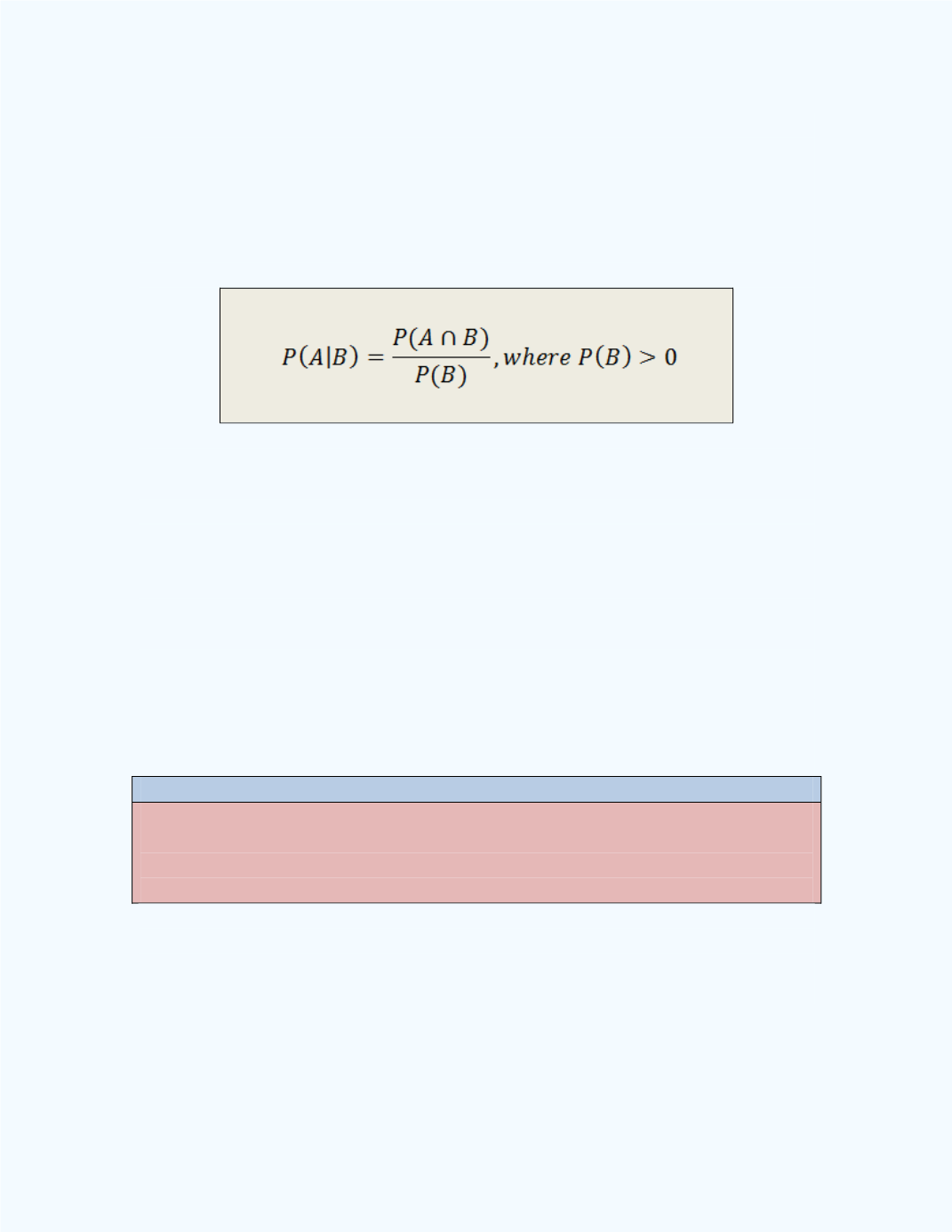
Rule 8:
The conditional probability of an event
A
, given that event
B
has
occurred, is computed from the following formula:
Example 7-21:
In a sample of 100 visitors to a city, 64 said they were on a
vacation trip, 28 said they were on a business trip, and 10 said they were
“killing two birds with one stone” by combining their business trip with their
vacation. If a visitor from this sample is selected at random, what is the
probability that the visitor is on a business trip given that the visitor is on
vacation?
Solution:
Let
B
be the event that the visitor is on a business trip. Let
V
be
the event that the visitor is on vacation. Then, we need to compute
P
(
B
|
V
).
From the information given in the problem,
P
(
B
) = 0.28,
P
(
V
) = 0.64, and
P
(
B
V
) = 0.1. Thus,
P
(
B
|
V
) =
P
(
B
V
) /
P
(
V
) = 0.1/0.64 = 0.15637
(correct to four decimal places).
Note:
In finding a conditional probability, we restrict the sample space to the event
on which we condition.
In
Example 7-21
, we are restricting the sample space to the event
V
.
Figure
7-19
shows this restricted sample space of the event
V
.
















