
Chapter 7: Probability
295
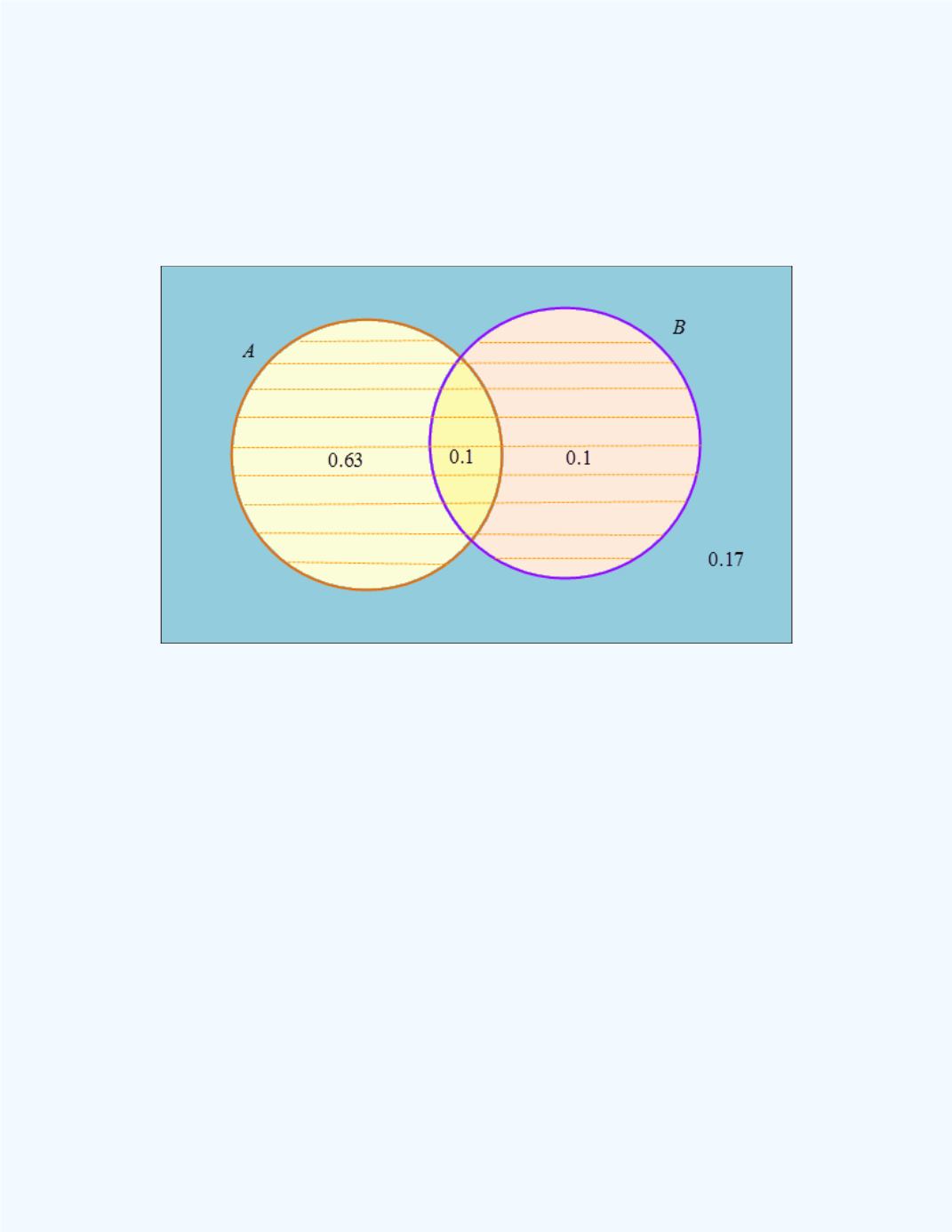
Solution:
Let
A
be the event that a student owns a smart phone, and let
B
be the event that a student owns an i-Pad. Thus,
P
(
A
) = 73/100 = 0.73,
P
(
B
) = 20/100 = 0.20, and
P
(
A
B
) =10/100 = 0.10. Thus,
P
(
A
B
) = 0.73 + 0.2 – 0.1 = 0.83. The Venn diagram depicting these
probabilities is presented in
Figure 7-17.
Figure 7-17:
Venn diagram for
Example 7-19
Example 7-20:
In a sample of 100 patients registering in an emergency
room, 70 said they have health insurance, 40 said this was their first trip to
the emergency room, and 10 said they
neither
have health insurance
nor
this
was this their first trip to the emergency room. Compute probabilities for
these events.
Solution:
Let
H
be the event that a patient has health insurance, and let
F
be the event that a patient visits the emergency room for the first time. Thus,
P
(
H
) = 70/100 = 0.7,
P
(
F
) = 40/100 = 0.4, and
P
{(
H
F
)
c
} = 10/100 = 0.1.
From the complement rule we have
P
(
H
F
) +
P
{(
H
F
)
c
} = 1. Also,
P
(
H
F
) =
P
(
H
) +
P
(
F
) -
P
(
H
F
) . So substituting for
P
(
H
F
) in
P
(
H
F
) +
P
{(
H
F
)
c
} = 1, we have
P
(
H
) +
P
(
F
) -
P
(
H
F
) +
P
{(
H
F
)
c
} = 1.
Thus, 0.7 + 0.4 -
P
(
H
F
) + 0.1 = 1
















