
Chapter 8: Discrete Probability Distributions
331
Example 8-12:
Ten items are selected at random from a production line.
What is the probability of selecting
less than
3 defectives if it is known that
the probability of a defective item from this production system is 0.05?
Solution:
Let the number of defectives be represented by
X
. Then
X
will
be a binomial random variable with
n
= 10,
p
= 0.05 and varying
x
values.
The probability of selecting less than 3 defectives is equivalent to finding
P
(
X
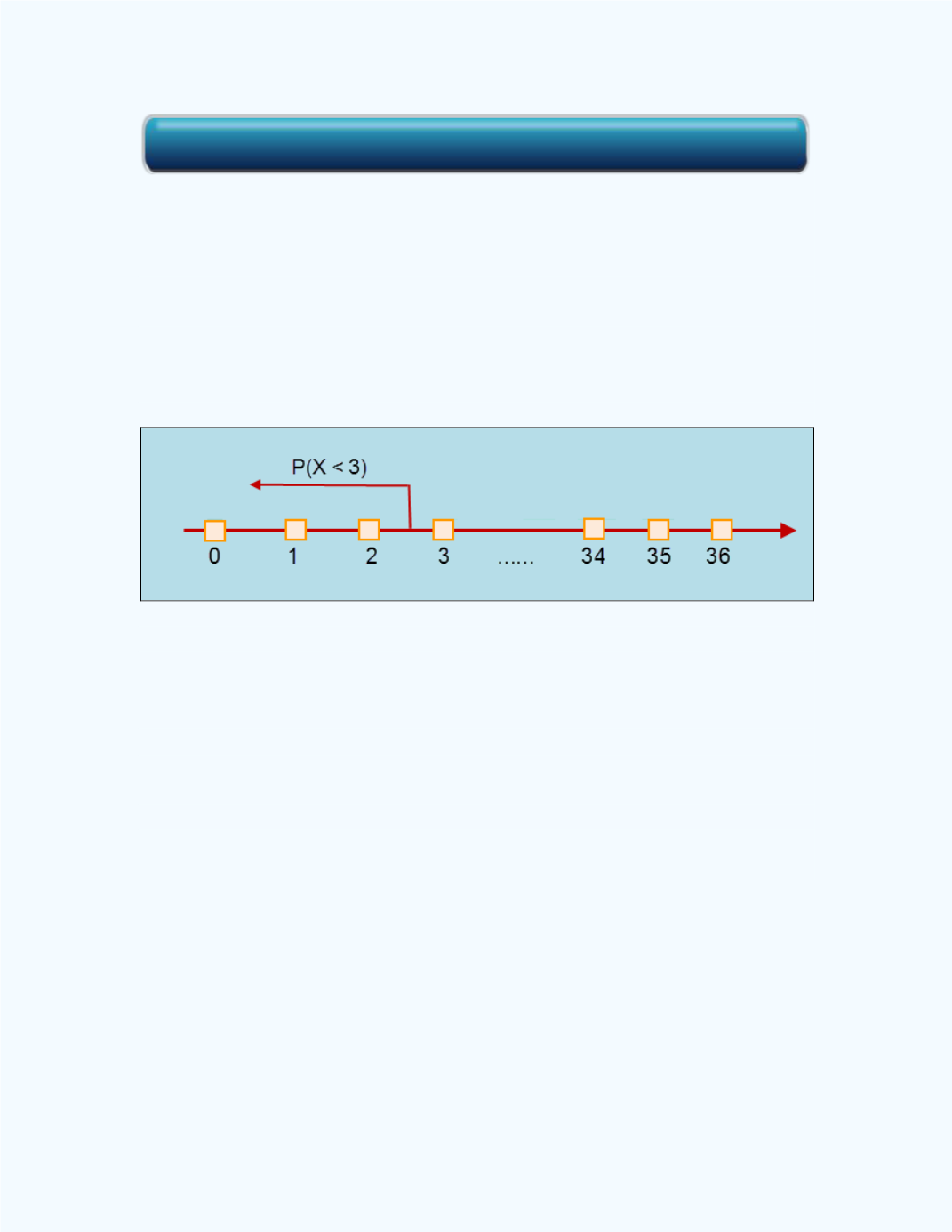
< 3). This situation is displayed in
Figure 8-12.
Figure 8-12:
Display of the event of
X
< 3
Now
P
(
X
< 3)
P
(
X
2) =
P
(
X
= 0 or
X
= 1 or
X
= 2) and since
X
= 0,
X
= 1,
X
=2 are mutually exclusive events, then
P
(
X
= 0 or
X
= 1 or
X
= 2)
=
P
(
X
= 0) +
P
(
X
= 1) +
P
(
X
= 2). Thus,
P
(
X
< 3) =
P
(
X
2) = 0.5987 +
0.3151 + 0.0746 = 0.9884 correct to four decimal places.
We can use the
Binomial Probability Distribution
workbook to help with
the computations.
Figure 8-13
shows the output for
Example 8-12
.
Click here for the Binomial Probability Distribution Workbook















