
336
Chapter 8: Discrete Probability Distributions
Solution:
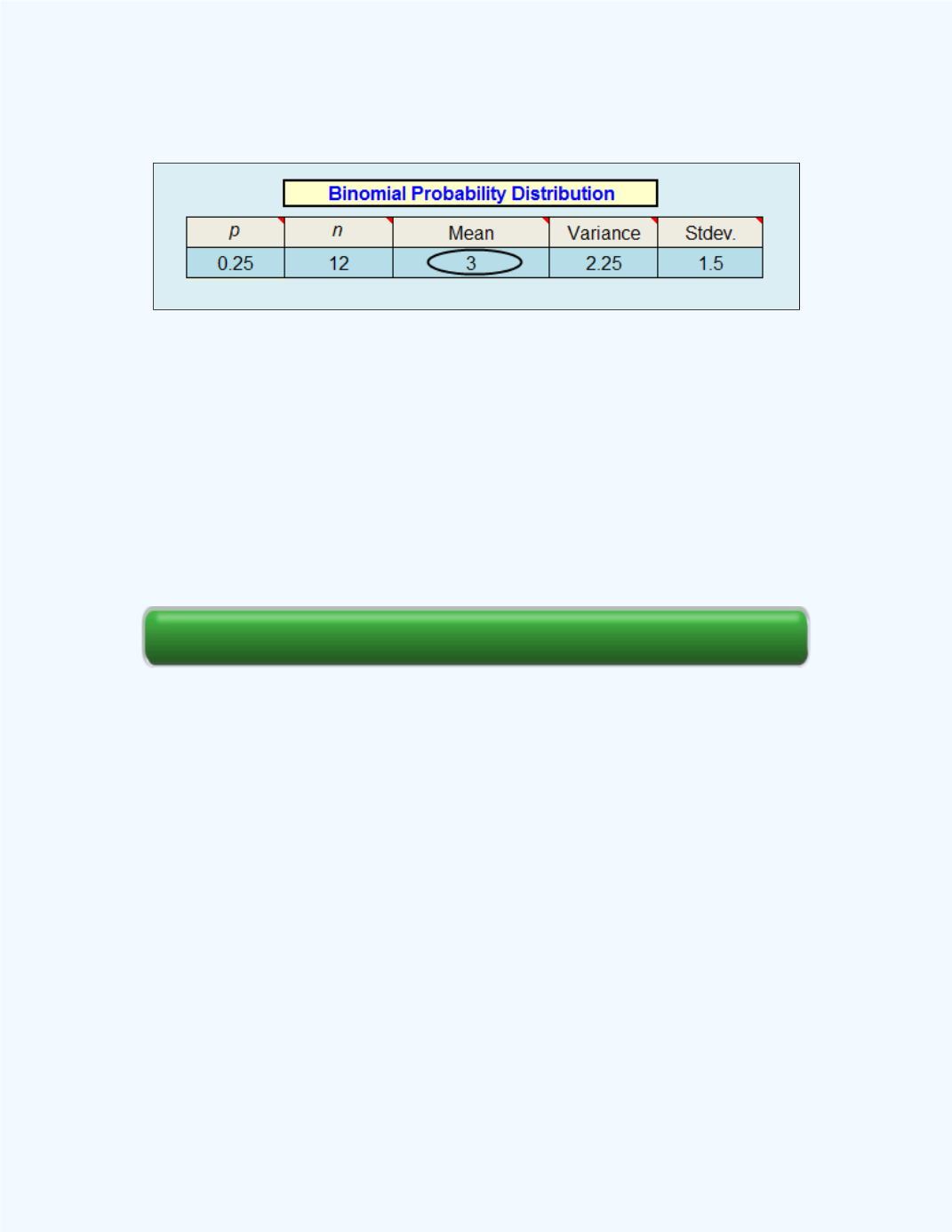
The workbook output is shown
in Figure 8-16.
Figure 8-16:
Display of the Binomial Distribution
Workbook for
Example 8-16
Example 8-15
requires us to determine the mean
. From
Figure
8-15
the mean
= 3. Observe that this value is the same as that obtained in
Example 8-15
.
Section Review
8-7 The Geometric Probability Distribution
Consider an experiment in which the properties for a binomial experiment
are satisfied, with the exception that the trials will be repeated
until the first
success occurs
. That is, on each trial, we have two possible outcomes
(success or failure); trials are independent; the probability of success is fixed
from trial to trial and is denoted by
.
We will let
X
= number of trials on which the first success occurs.
We will let
= probability of a failure outcome.
The experimental design of observing the first success on the
trial is
graphically displayed in
Figure 8-17
. An experiment which satisfies these
described conditions is called a geometric experiment.
e-Self Review















