
Chapter 12: Hypothesis Tests – Large Samples
513
12-2 Some Terms Associated with Hypothesis Testing
When we have an opinion about a characteristic of a population, we may
need to verify whether the opinion is true or not. We may propose a
statement about that opinion and through some process try to verify whether
the statement is correct through some process. Such a proposed statement is
usually referred to as a hypothesis which we would have to test for
validation of the opinion. As such every situation that requires a hypothesis
test starts with a statement of a hypothesis.
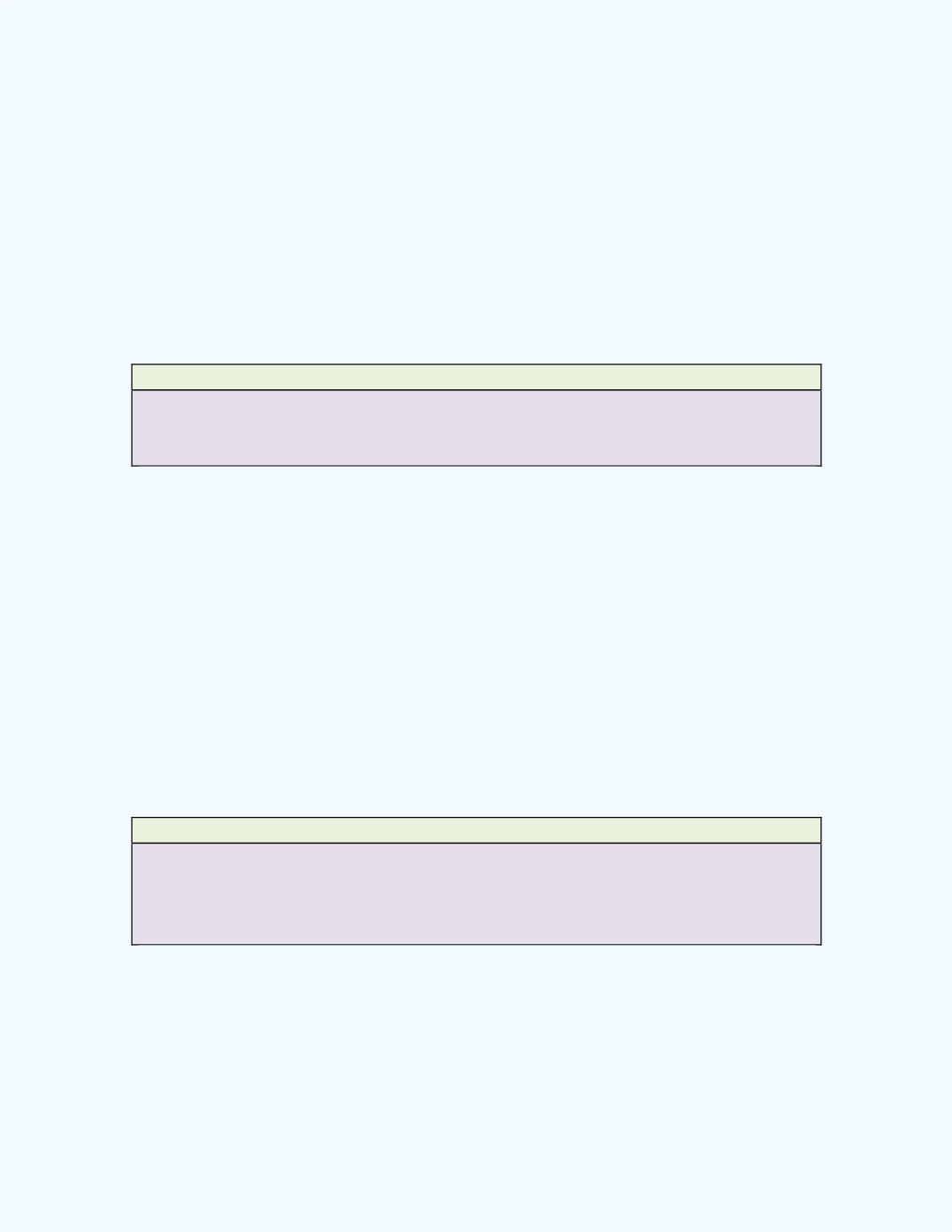
Definition: Statistical Hypothesis
A statistical hypothesis is an opinion about a population parameter.
Example 12-1:
A researcher feels that the proportion of alligators
constitutes 30 % of the reptile population in a particular ecosystem. What
statistical hypothesis is the researcher proposing?
Solution:
The opinion expressed by the researcher is that 30 percent of the
entire population of reptiles in the ecosystem is alligators. The parameter of
interest here would be the proportion of alligators in the ecosystem.
When dealing with hypothesis, one will have to deal with two types. These
two types of statistical hypotheses area the
null hypothesis
and the
alternative hypothesis
.
First we will define what we mean by a null
hypothesis.
Definition: Null Hypothesis (
H
0
)
The null hypothesis states that there is no difference between a parameter (or
parameters) and a specific value.
Notation:
The null hypothesis is denoted by
















