
Chapter 12: Hypothesis Tests – Large Samples
515
We will need to compute, from sample data, a
test value
or a
test statistic
in
order to make the decision. The formula that is used to compute this value
will vary depending on the statistical test.
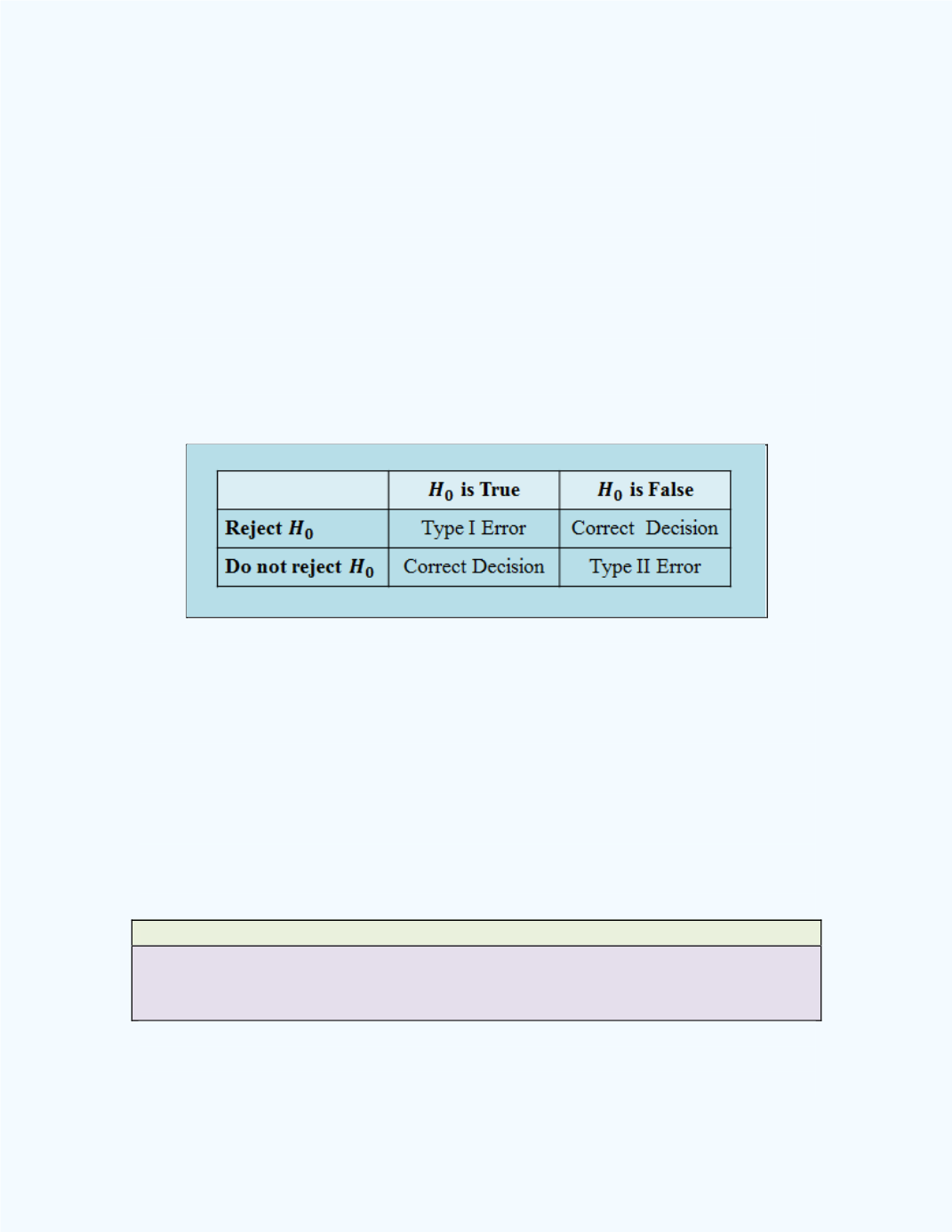
Possible Outcomes for a Hypothesis Test
When a test is done, there are four possible outcomes. These outcomes are
summarized in
Table 12-1
along with the types of errors one can commit
when performing hypothesis tests.
Table12-1:
Possible Outcomes and Types of Errors
Committed when Performing a Hypothesis Test
Observe that there are two possibilities for a correct decision and two
possibilities for an incorrect decision.
Types of Error for a Hypothesis Test
From
Table 12-1
,
we can observe that there are two ways of making a
mistake when doing a hypothesis test. These two errors are called a
Type I
error
and a
Type II error
.
Following is the definition of a Type I error.
Definition: Type I Error
A Type I Error occurs if a null hypothesis which is true is rejected.
Next, we define a Type II error.
















