
Chapter 16: One-Way Analysis of Variance
747
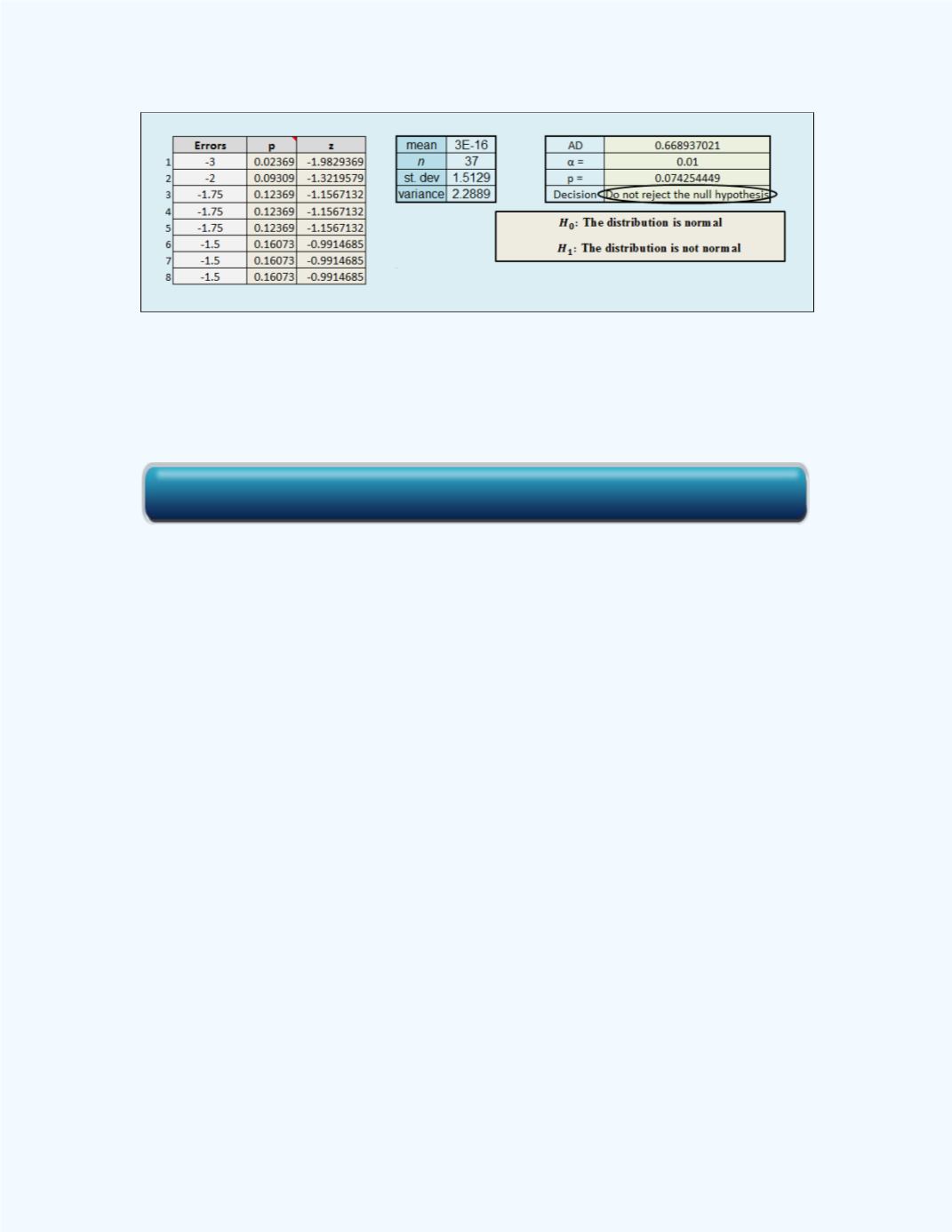
Figure 16-24:
Normality Test for Errors in
Example 16-12
Note that the Normal Probability Plot for the errors has a linear pattern
which supports the assumption of normality for the errors.
We can use the information in
Figure 16-24
to present a test for the
normality assumption. Use a level of significance of
= 0.01.
: The errors have a normal distribution.
: The errors are not normally distributed.
.
:
P
-value = 0.0743 (to four decimal places).
D
.:
For a significance level 0.01, reject the null hypothesis if the
computed test statistic value,
P
-value = 0.0743 <
= 0.01.
Conclusion
: Since 0.0743 > 0.01, do not reject the null hypothesis. That
is, at the 1 percent level of significance, there is not enough sample evidence
to reject the null hypothesis of normality of the distribution for the errors.
Figure 16-25
shows the normality plot for the errors. Observe the straight
line nature of the probability plot. This straight line nature of the probability
plot is an indication that the errors are normally distributed.
Click here for the Test for Normality Workbook















