
Chapter 8: Discrete Probability Distributions
323
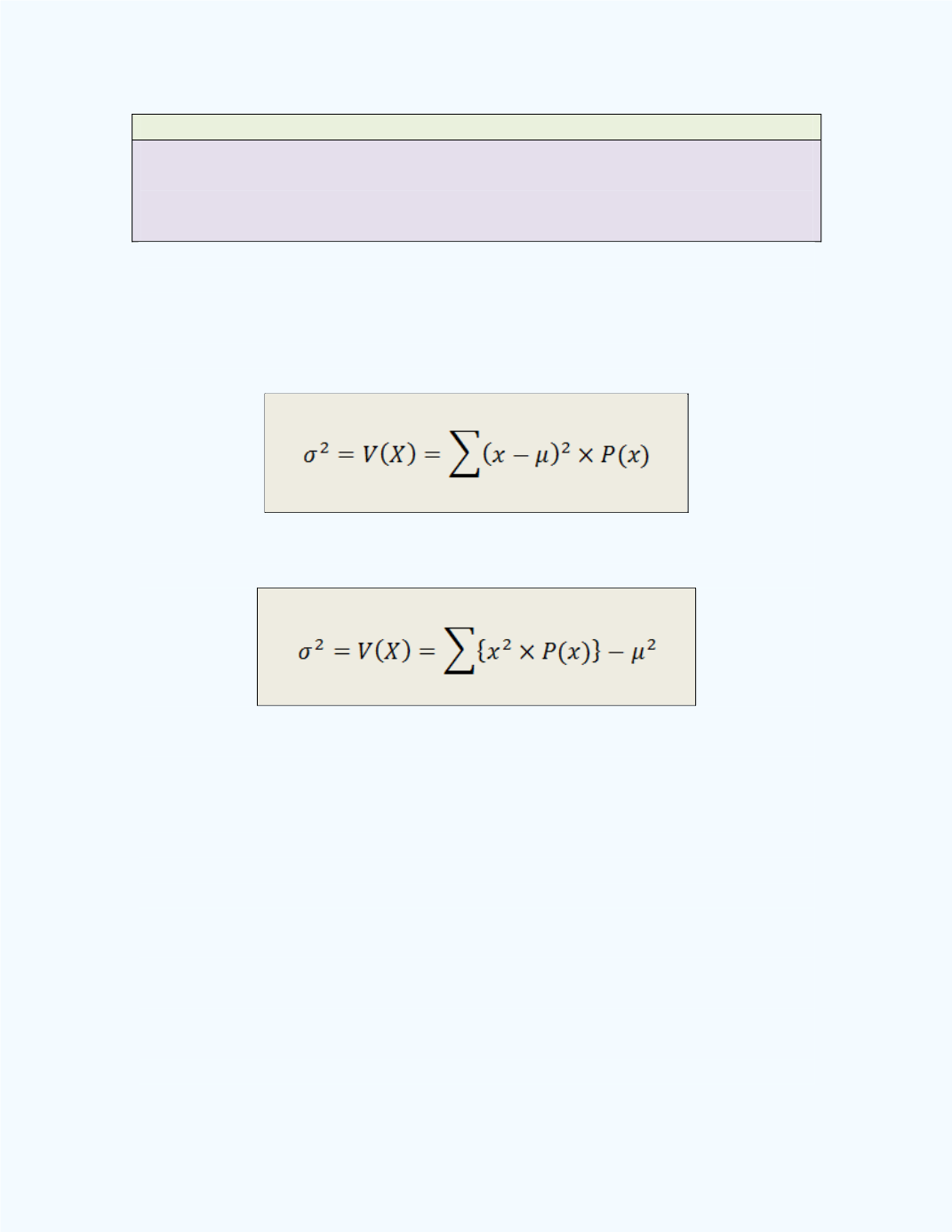
Definition: Variance for a Discrete Random Variable
The variance for a discrete random variable
X
measures the spread of the
random variable about the expected value (mean
).
The variance is usually denoted by
(read as “sigma square”) or V(
X
) and
is obtained by computing the expected value of the squared deviations from
the mean
. The formula is given next. The weights here will be the values
of the probabilities associated with the values of the random variable.
An equivalent computational formula for the variance is given as
In both equations,
is the expected value for the random variable
X
.
Also, in the above formula, the summation is only for
} over
all the
x
values. The variance for a probability distribution is equal to its
population variance.
Example 8-6:
What is the variance of the winnings for a raffle with a first
prize of $1000, a second prize of $500, and a third prize of $300 if 1,000
tickets are sold?
Solution:
Let the winnings for the raffle be represented by the random
variable
X
. First we need to compute the mean,
for
X
. In order for us to
complete the computation for
we will have to derive the probability
distribution for
X
. If we assume that the tickets are drawn at random without
replacement, then the probability of winning the first prize will be 1/1000;
















