
Chapter 9: The Normal Probability Distribution
381
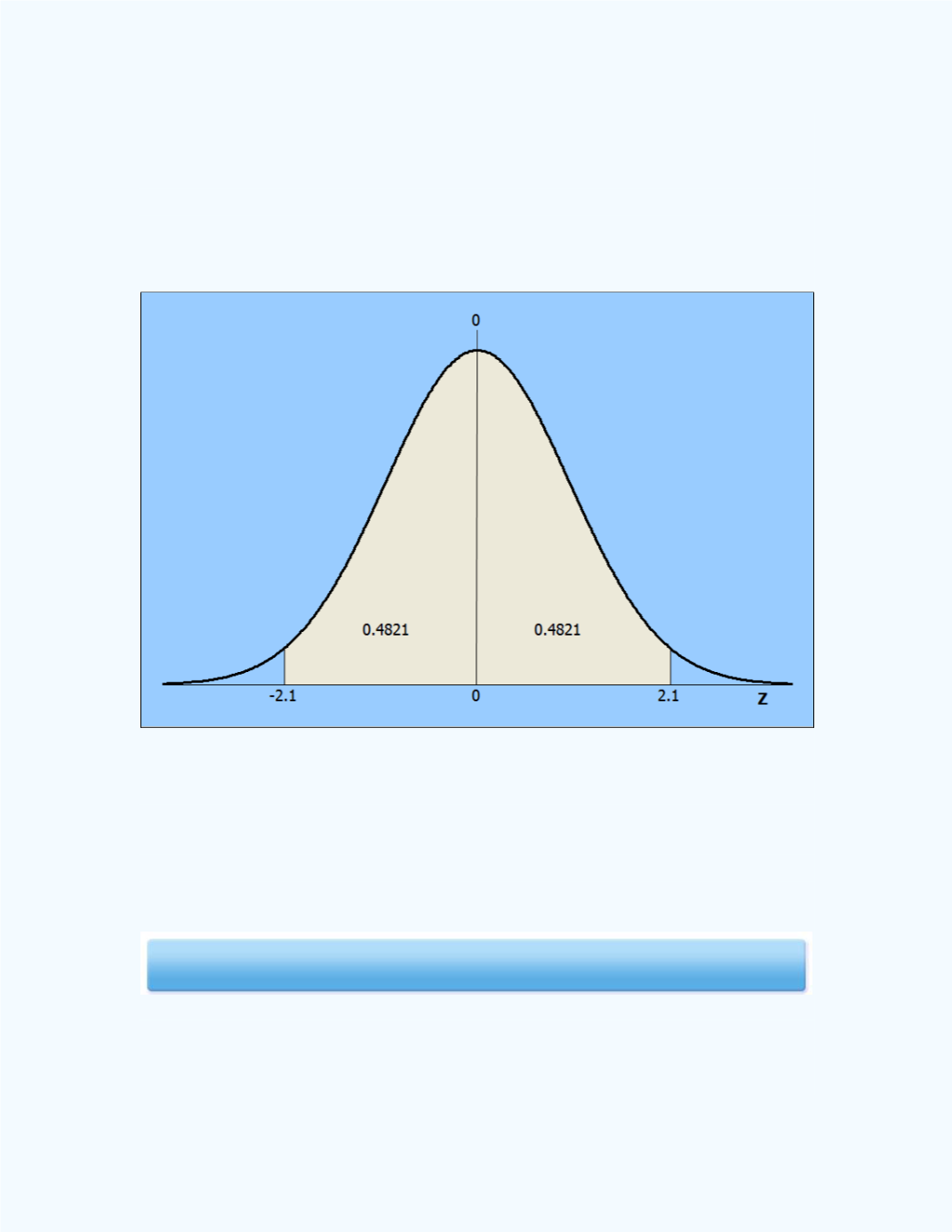
If you would like to use a
-table to help solve this problem, we can use the
symmetric property of the standard normal distribution since the table gives
probability for only positive
-values. So, from the symmetry of the
distribution,
P
(-2.1
0) =
P
(0
2.1). From the standard normal
tables, for
= 2.1, the corresponding value is 0.4821. Thus,
P
(-2.1
0)
= 0.4821 as well. The symmetric solution is displayed in
Figure 9-21
.
Figure 9-21:
Display of the Symmetric solution for
P
(-2.1
z
0)
Note:
We could have also used the cumulative probability up to -2.1 and
then subtract from 0.5 since the right end point for the required interval is
zero. Now
P
(
-2.1) = 0.0179. Thus
P
(-2.1
0) = 0.5 – 0.0179 =
0.4821.
Example 9-3:
Find the area under the standard normal distribution curve
to the right of
= 1.35.
Click here for the z-Table Workbook















