
418
Chapter 10: Sampling Distributions and the Central Limit Theorem
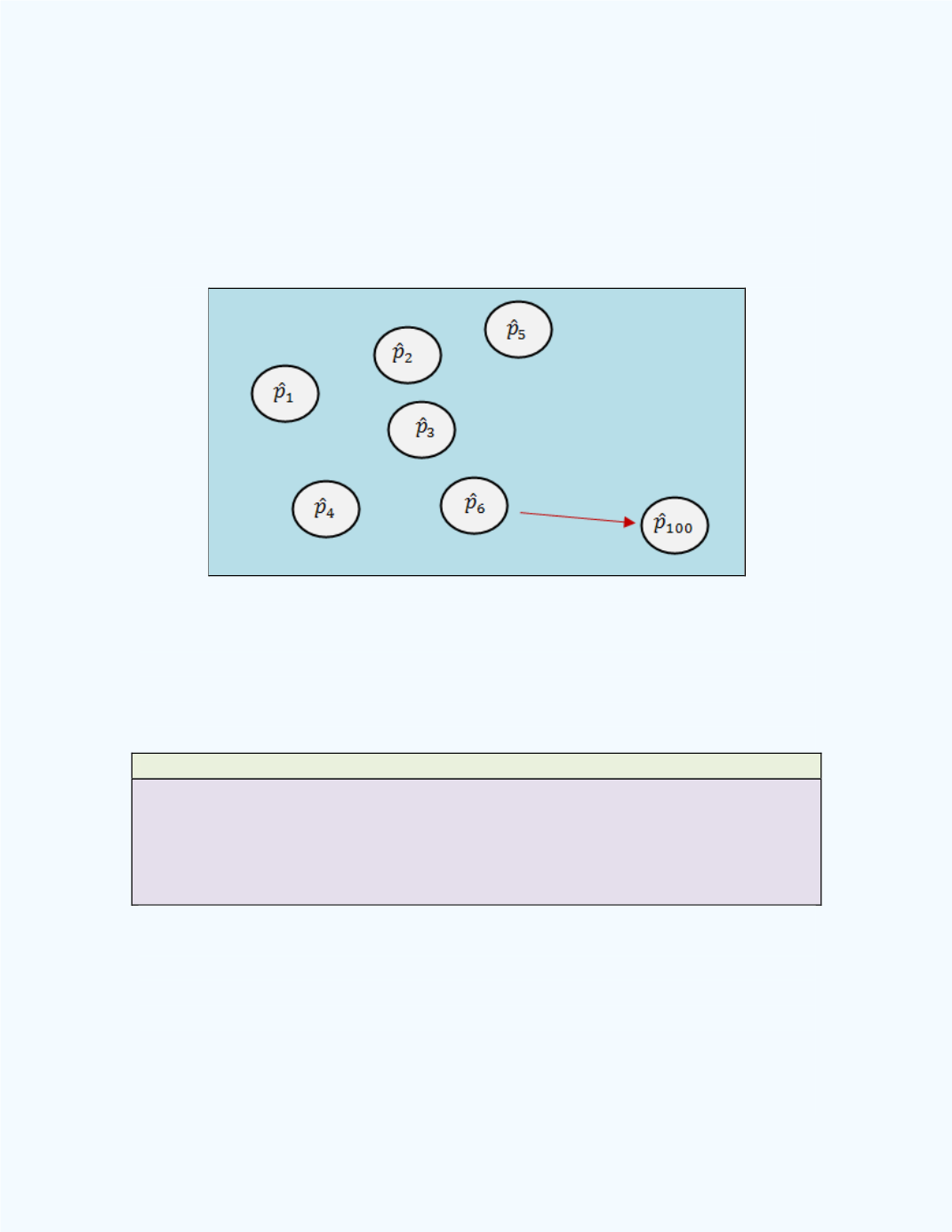
If we were to select another random sample of size 50, we would most likely
obtain a different value for the sample proportion. If we selected 100
different samples of the same sample size and compute these sample
proportions, we should not expect these values to all be the same. That is,
there will be some variability in these computed proportions. Pictorially, the
situation is demonstrated in
Figure 10-2
.
Figure 10-2:
Sample Proportions for One Hundred
Samples of Size 50
These 100 sample proportions constitute a
sampling distribution
of a
sample proportion.
Definition: Sampling Distribution of a Sample Proportion
A sampling distribution of a sample proportion is a distribution obtained by
using the proportions computed from random samples of a specific size
obtained from a population.
In order to investigate properties of the sampling distribution of a sample
proportion, simulations of the situation can be done. In this illustration, 100
samples of size 50 were generated using the
Generating Sample
Proportions
workbook.
The distribution used in the simulation was the binomial distribution with
parameters
= 50 and
= 0.89. This assumed distribution is reasonable,
















