
460
Chapter 10: Sampling Distributions and the Central Limit Theorem
Find the probability that Method 1, on average, took longer than Method 2 to
assemble the product. That is, we need to determine
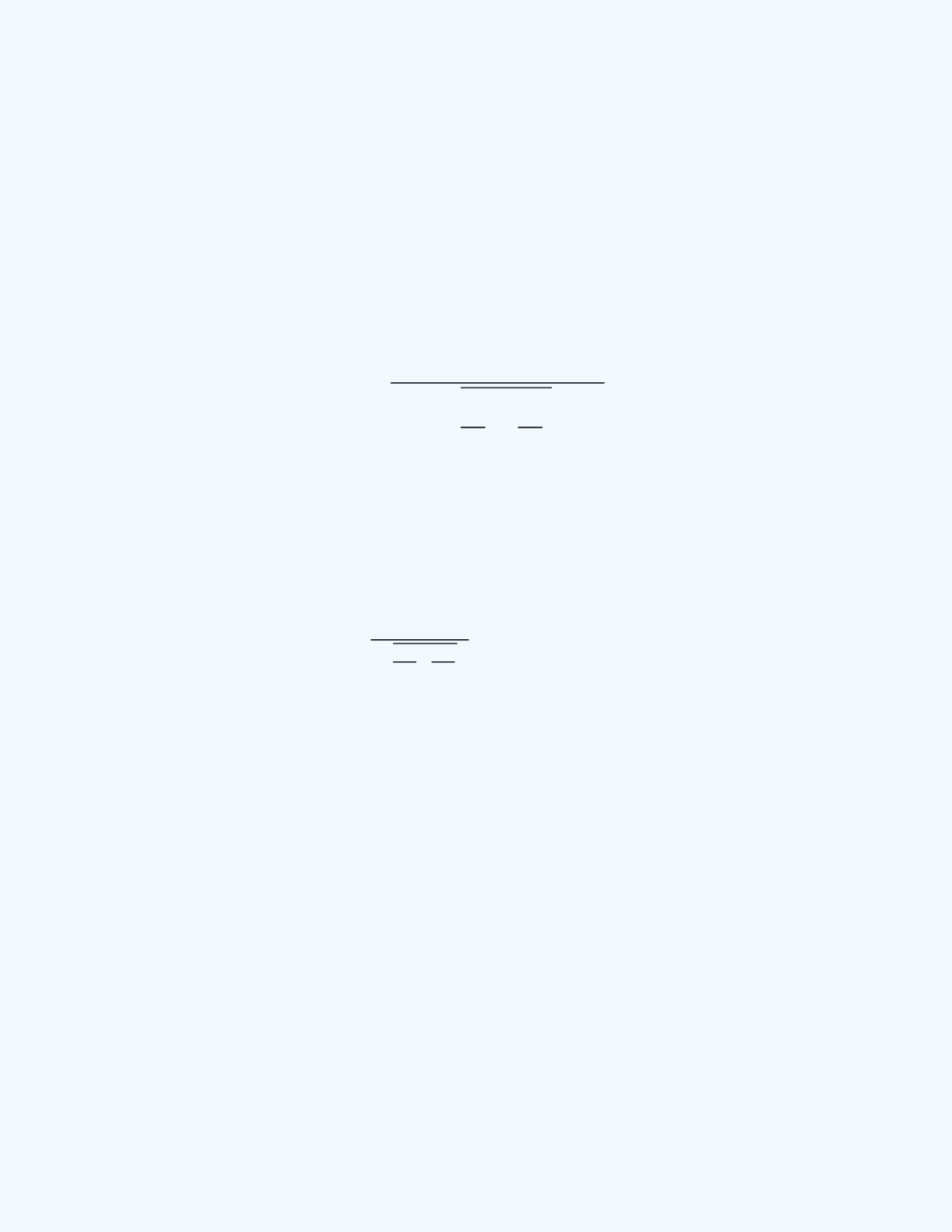
̅
̅
). This is
equivalent to
̅
̅
0).
Solution:
Fromthe information given, we need to determine
(̅
̅
) ̅
̅
0)
.
We have
= 45,
= 55,
= 16,
=
19,
= 85, and
= 76. Since we need to determine
̅
̅
0), we
can substitute into
̅
̅
√
to compute the corresponding
-score.
Note:
We are using the sample
variances since the population variances are unknown and both
30 and
30.
Substituting we get
√
= -2.5712
So,
̅
̅
)
̅
̅
0) =
-2.5712) = 0.9949 from the
Normal Distribution
workbook. This is a rather large probability, and so if
one is given the choice of the two methods of assembling the product, one
should chooseMethod 2. It seems, based on this probability value,
Method 2 is more effective.
Figure 10-32
displays the output from the
Normal Probability Distribution
workbook showing the computed
probability.
















