
Chapter 12: Hypothesis Tests – Large Samples
549
̂
̂
√ ̂ ̂ (
)
D.R
: For a specified significance level
, reject the null hypothesis if
the computed test statistic value
is greater than +
.
Conclusion
: ……….
Note:
This is a right-tailed test because the direction of the inequality sign
in the alternative hypothesis is to the right.
Example 12-9
:
Over the past several years, there have been aggressive
anti-smoking campaigns. One might ask if a difference exists in the
proportion of smokers from a 2010 population versus those of the present
2012 population. We would clearly expect the proportion of smokers to be
greater in the 2010 population.
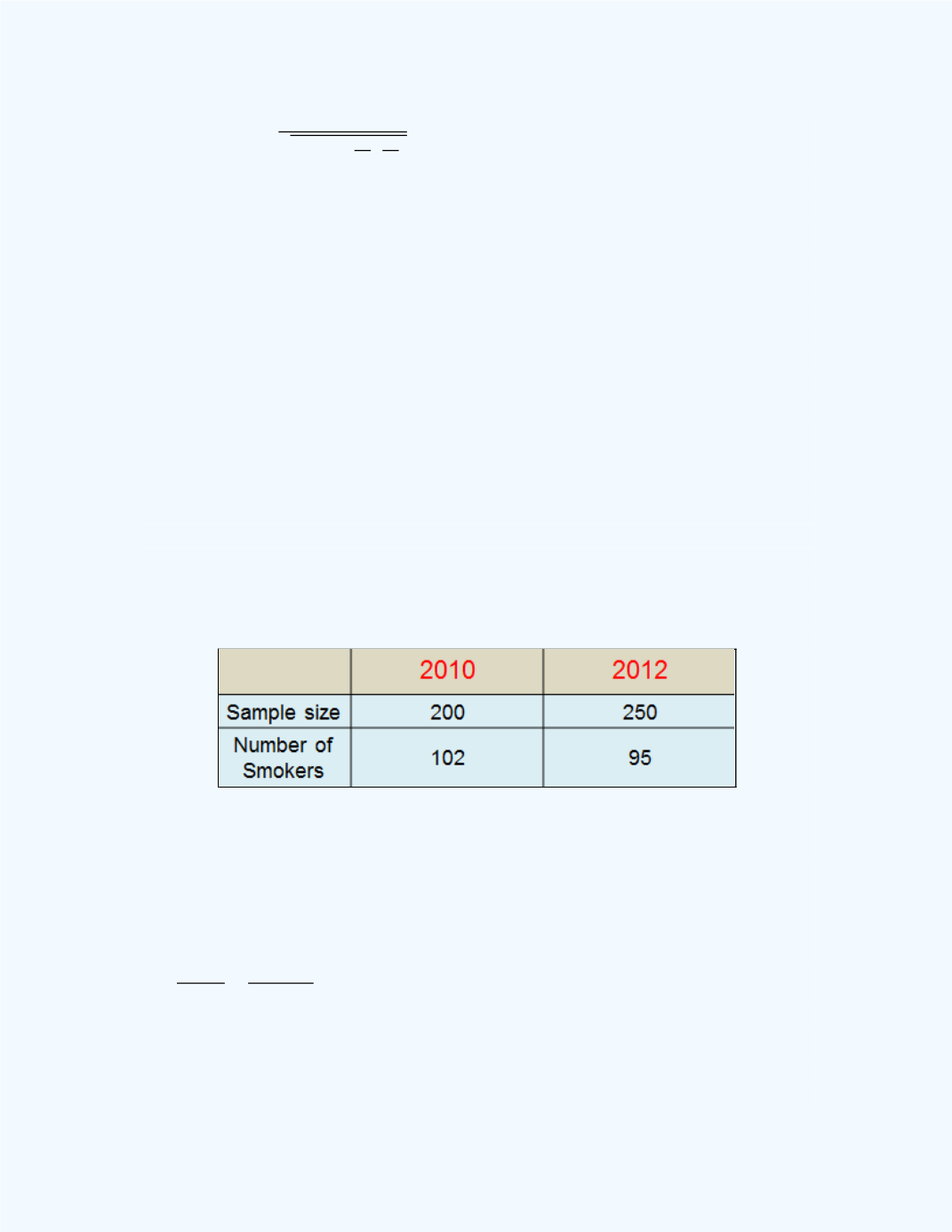
Table 12-2
shows the results of a study which try to address this question.
Table 12-2:
Data for
Example 12-9
Use the classical approach to test, at the 5% level of significance, whether
the campaigns have decreased the proportion of smokers from 2010 to 2012.
Summary information:
Let
be the proportion of smokers from the 2010
group. Let
be the proportion of smokers from the 2012 group.
From the information given,
= 200,
= 250,
̂
= 0.51,
̂
= 0.38,
̂
=
=
= 0.4378,
= 0.05,
= 1.645.
Solution:
:
(
p
1
-
p
2
0)
















