
670
Chapter 15: Chi-Square Tests
Note:
The chi-square goodness-of-fit test is always a right-tailed test.
Example 15-3:
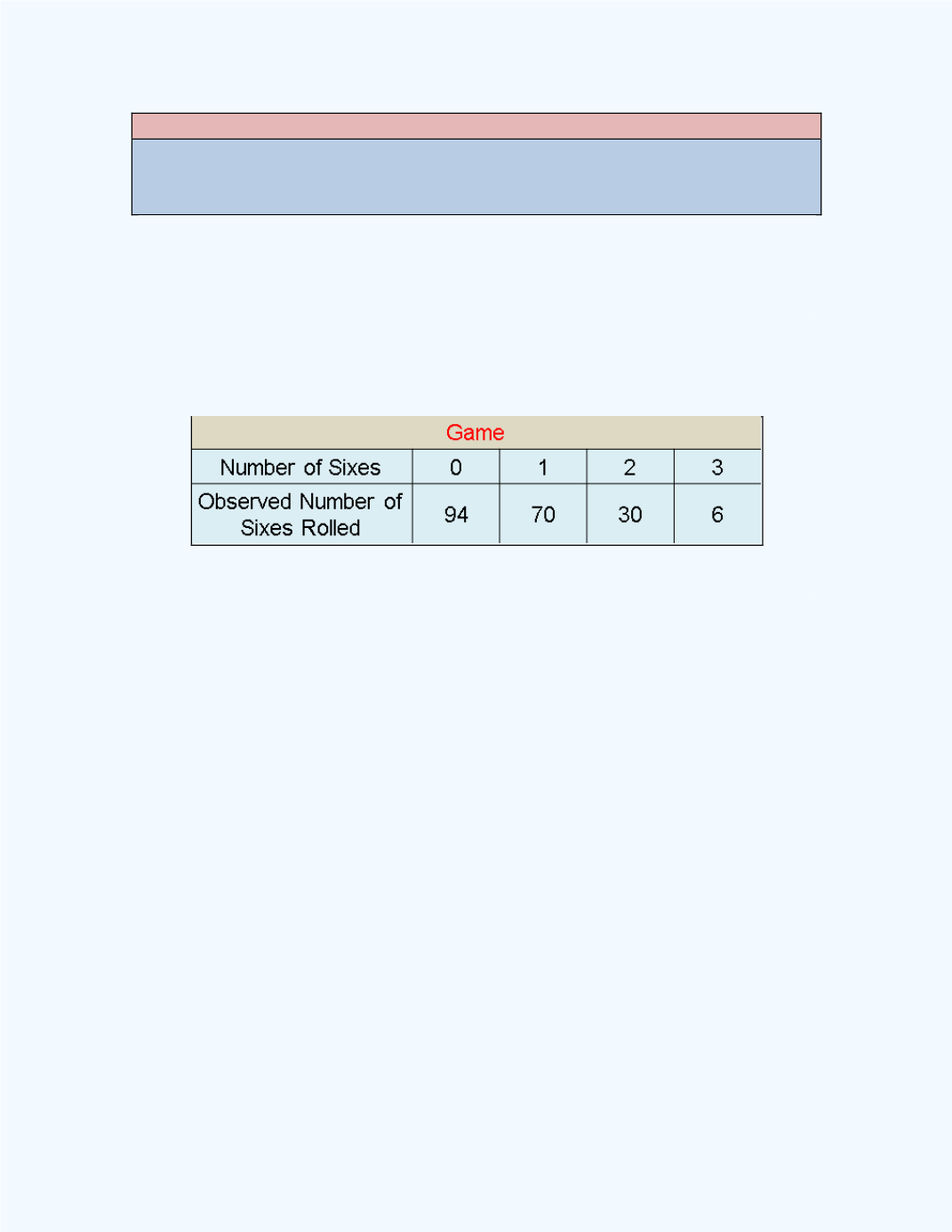
A game involves rolling a die three times. The winnings
are related to the total number of sixes rolled. The following table shows the
number of sixes rolled after a person plays the game 200 times:
Table 15-1:
Table with Observed frequencies for
Example15-3
Test to determine whether the die is fair at the 5% level of significance.
What can you conclude?
Solution:
For a fair die, one would expect the probability of observing a 6
on any given roll to be 1/6. If we assume that the rolls are independent, then
the number of observed sixes in the three rolls of the die will be a binomial
random variable with
= 3 and
= 1/6. To determine whether the die is
fair, one may compare the observed results in the 200 rolls with the results
expected under this binomial distribution.
To obtain the probabilities for the number of sixes rolled we need to use the
binomial distribution with
= 3,
= 1/6 and
x
= 0, 1, 2, 3. We can use the
Binomial Probability Distribution
workbook (from Chapter 8). The
computed probabilities are shown in
Figure 15-9
.
















