
Chapter 1: Introduction and Graphical Displays
21
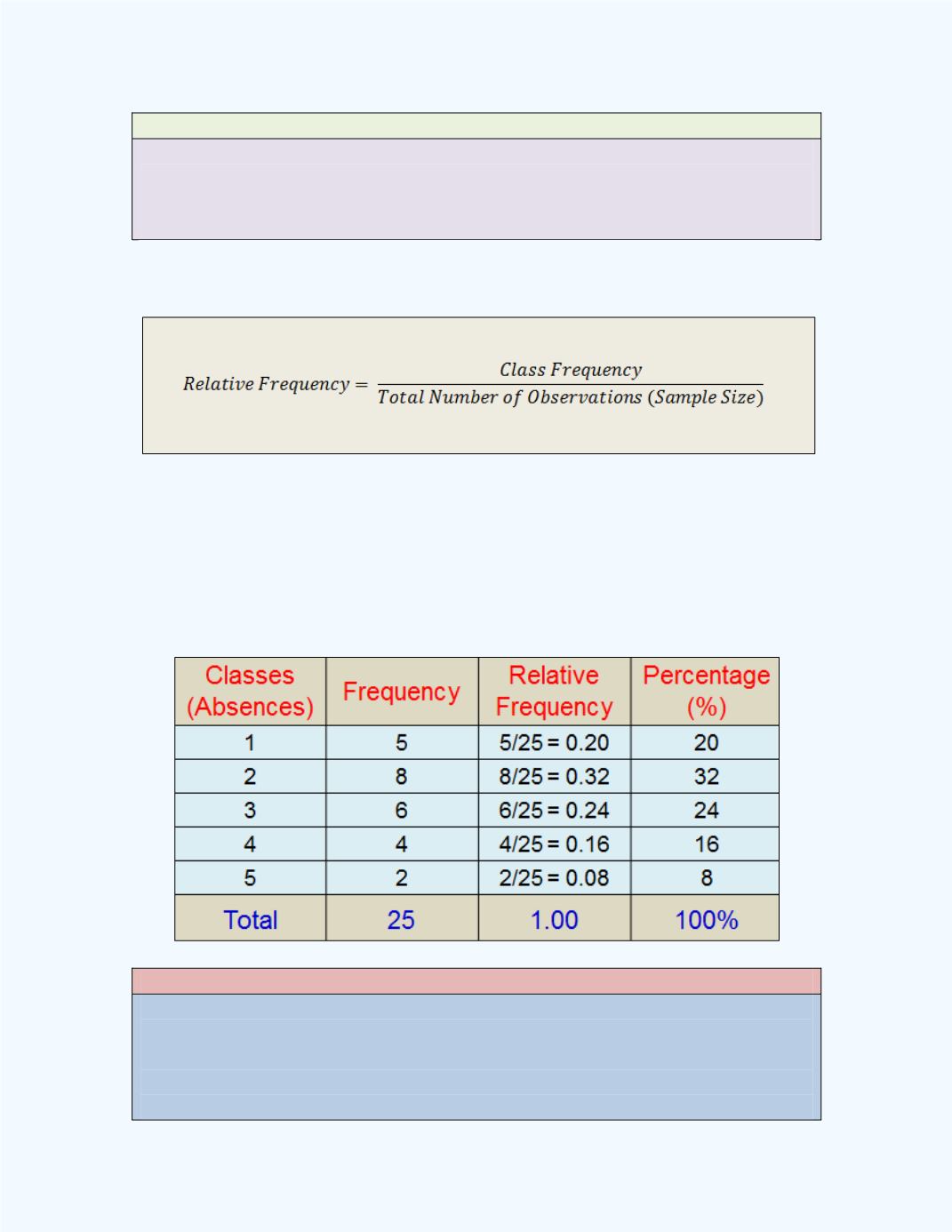
Definition: Relative Frequency
The relative frequency for any class is obtained by dividing the frequency
for that class by the total number of observations or the sample size.
That is,
The frequency distribution in
Table 1-3
uses the data in
Example 1-2
and
displays the relative frequencies as well as the corresponding percentages for
each class.
Table 1-3:
Frequency Distribution Along with
Relative Frequencies for
Example 1-2
Note:
Sometimes frequency distributions are presented with the cumulative
frequencies and the cumulative relative frequencies as well, in addition to
the frequencies, for the different classes.
















