
364
Chapter 9: The Normal Probability Distribution
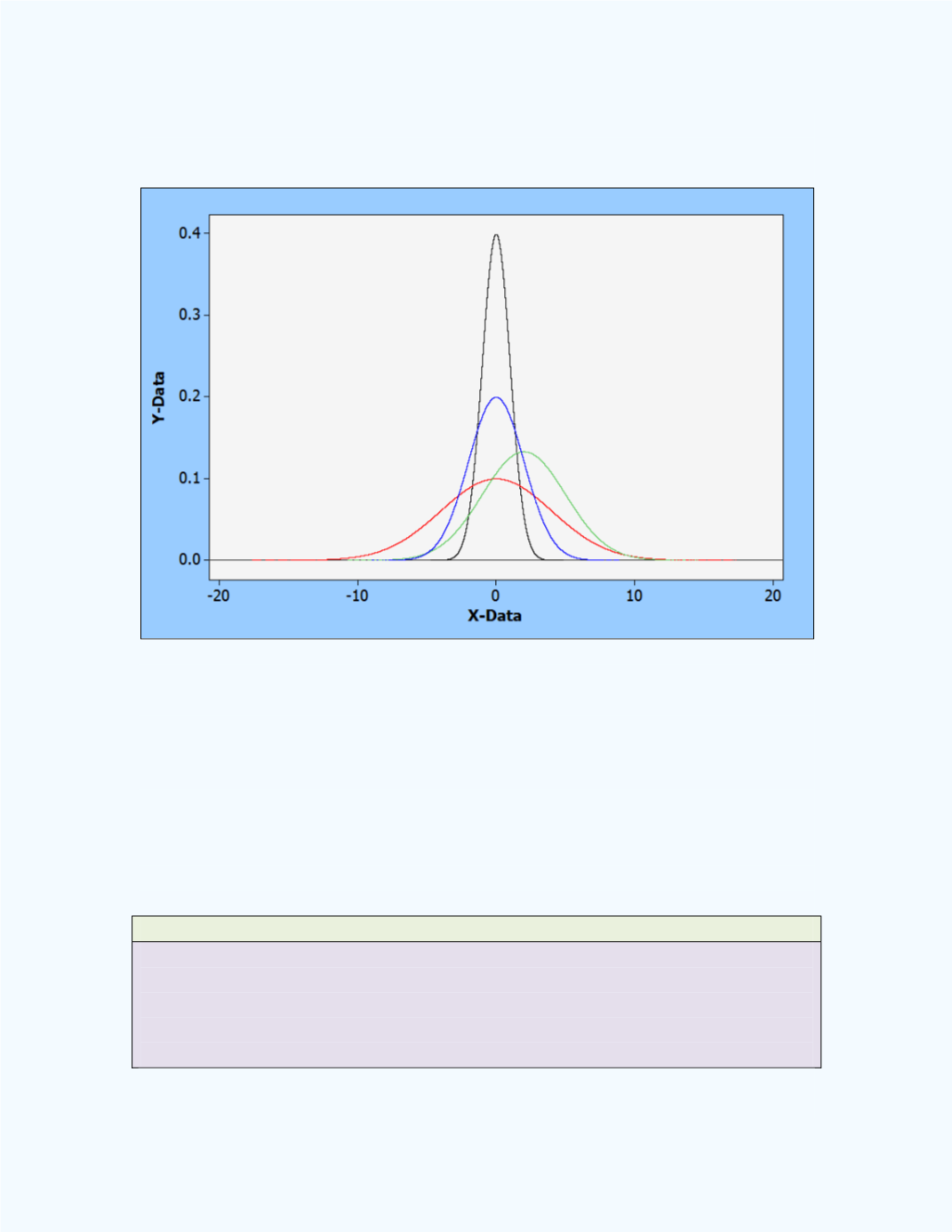
of normal distribution curves are shown in
Figure 9-5
. Observe the bell-
shaped nature of the graphs.
Figure 9-5:
Examples of normal probability distributions
Because of the symmetry of the normal distribution, the mean, median, and
mode will all be located at the center and will be equal to each other. Note
that these normal curves have similar shapes but are located at different
points along the
-axis. Also, the larger the standard deviation, the more
spread out is the distribution, and the curves are symmetrical about their
respective mean value. Also, the curve never reaches the x-axis in either
direction. Following is a definition for the normal distribution.
Definition: Normal Distribution
A normal distribution is a continuous, symmetrical, bell-shaped distribution
of a normal random variable which is defined over the entire real number
line for a specific mean and standard deviation.
















