
Chapter 3: Measures of Variability
125
Example 3-13:
The mean ACT mathematics score for class of college
freshmen was 21 with a standard deviation of 4. The average age (in years)
of these freshmen was 19.2 with a standard deviation of 1.1. Compare the
variations of the two variables. Assume that the class of freshmen represents
the population of all freshmen on the college campus.
Solution:
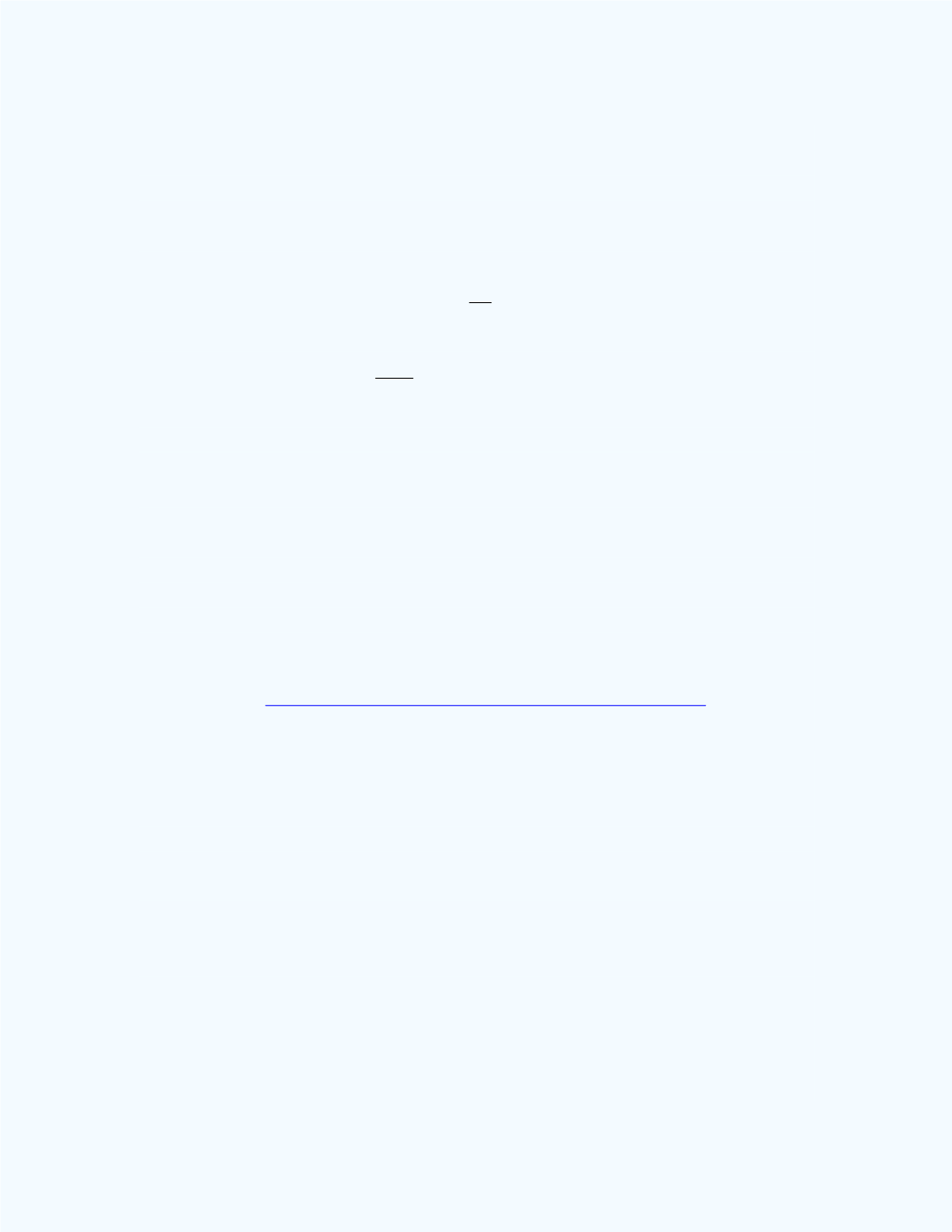
(ACT Math Score) =
% 0476 .19%100
21
4
(Age) =
% 7292 .5%100
2.19
1.1
Since the
CV
is larger for the ACT mathematics score then there is more
variability in the ACT scores relative to the variability of the ages.
Note:
If we had data we could use the
Basic Statistics
workbook to find
these coefficient of variations.
Example 3-14:
Table3-2
gives the total storms classified as “Killer
Tornadoes” and the total fatalities as a result of these storms from 2000 to
2010.
Data Source
:
http://www.spc.noaa.gov/climo/torn/fataltorn.html















