
Chapter 10: Sampling Distributions and the Central Limit Theorem
439
Solution:
Observe that we know the distribution of the salaries to be
normal so the sample size does not matter when the Central Limit Theorem
for the Sample Means is applied. We need to determine
̅
<
44,200). Now,
= 45,000,
= 15,000,
= 25, and
√ ⁄
= 15,000/5 =
3,000.
We will solve by using the
Normal Probability Distribution
workbook
since the sample mean will be normally distributed with
= 45,000, and
standard deviation and
√ ⁄
= 15,000/5 = 3,000. Using the workbook, we
get
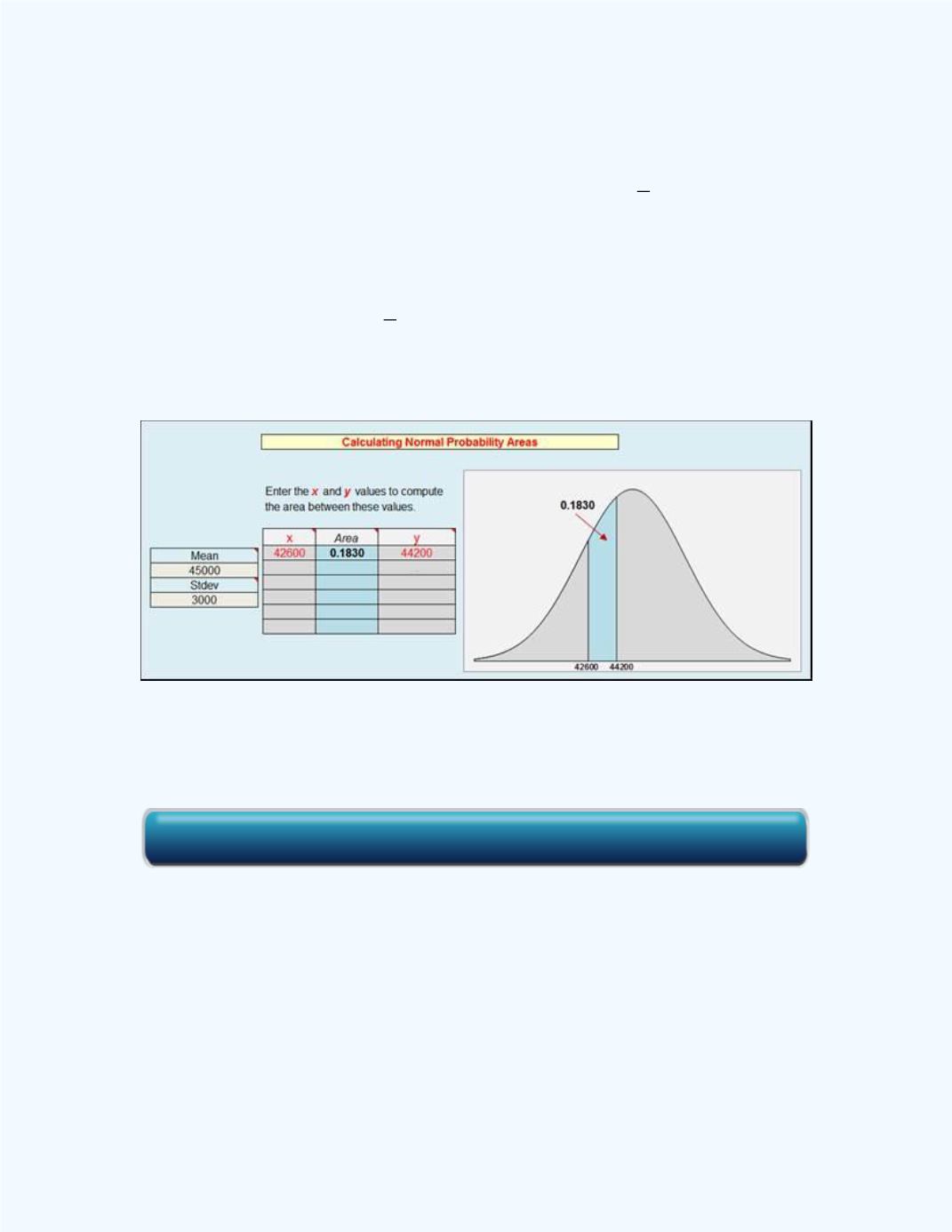
P
(42,600
̅
< 44,200) = 0.1830. This result is shown in
Figure 10-19
.
Figure 10-19:
The Normal Distribution Area for
P
(42,600
̅
< 44,200) in
Example 10-4
The
Sampling Distribution for the Sample Mean
workbook solution is
given in
Figure 10-20
. Bothworkbooks give the same result. Here we
assume that the sampling distribution is normally distributed as specified in
the problem.
Click here for the Normal Probability Distribution Workbook















