
442
Chapter 10: Sampling Distributions and the Central Limit Theorem
Definition: Sampling Distribution of the Difference Between Two
Independent Sample Proportions
A sampling distribution of the difference between two independent sample
proportions is a distribution obtained by using the difference of the sample
proportions computed from random samples obtained from the two
proportions.
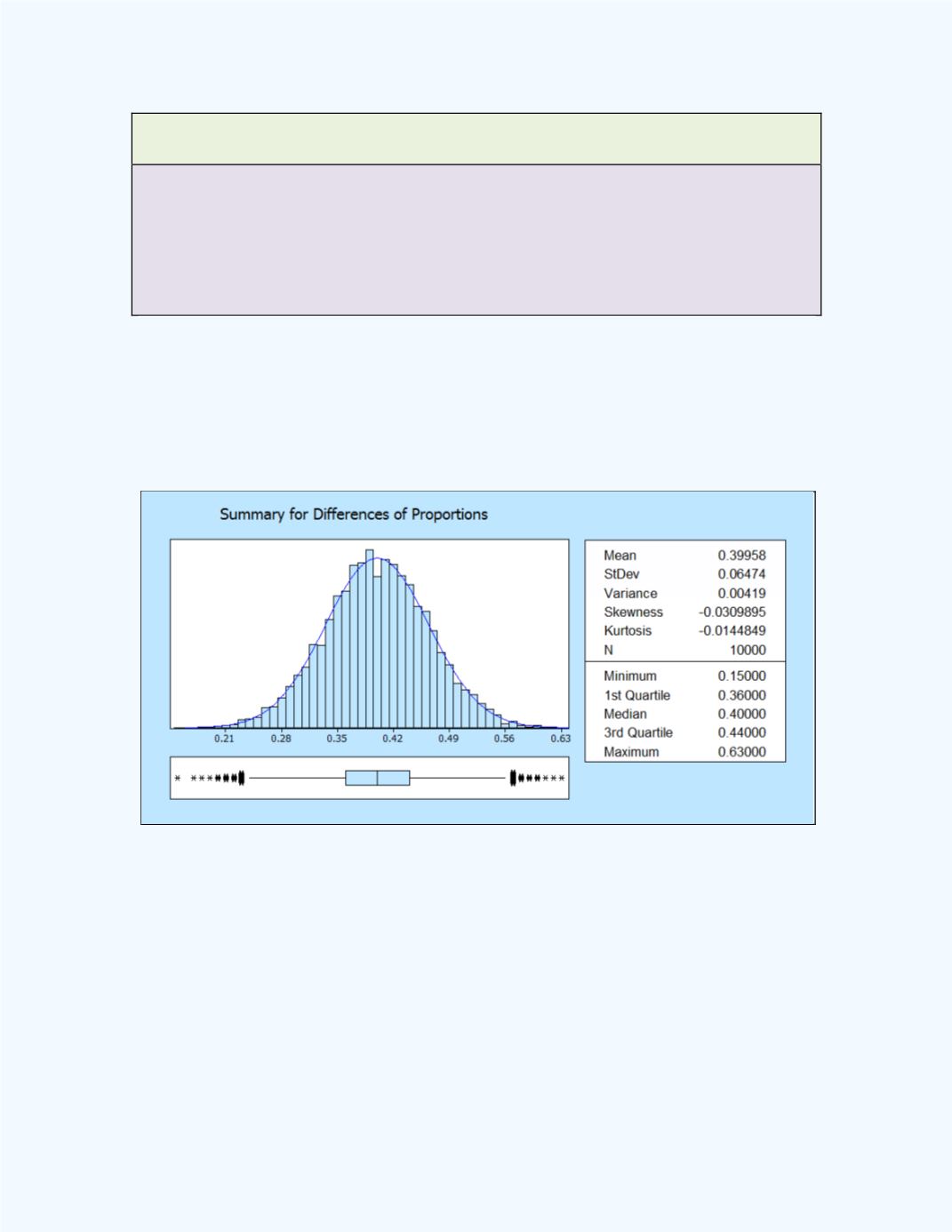
In order to investigate properties of the sampling distribution of the
difference between two sample proportions, simulations of the situation can
be done. Ten thousand samples of size of 100 were simulated from binomial
distributions with
= 0.7 and
= 0.3. The descriptive statistics for the
difference of the simulated proportions are shown in
Figure 10-22
.
Figure 10-22:
Descriptive Statistics of Simulation
For the Difference Between two Sample
Proportions
Let
̂
̂
represent the mean of the differences of the sample proportions,
and
̂
̂
represent the standard deviation of the differences of the sample
proportions. Table 10-7 shows some summary statistics for the 10,000
differences of the simulated sample proportions.
















