
Chapter 10: Sampling Distributions and the Central Limit Theorem
449
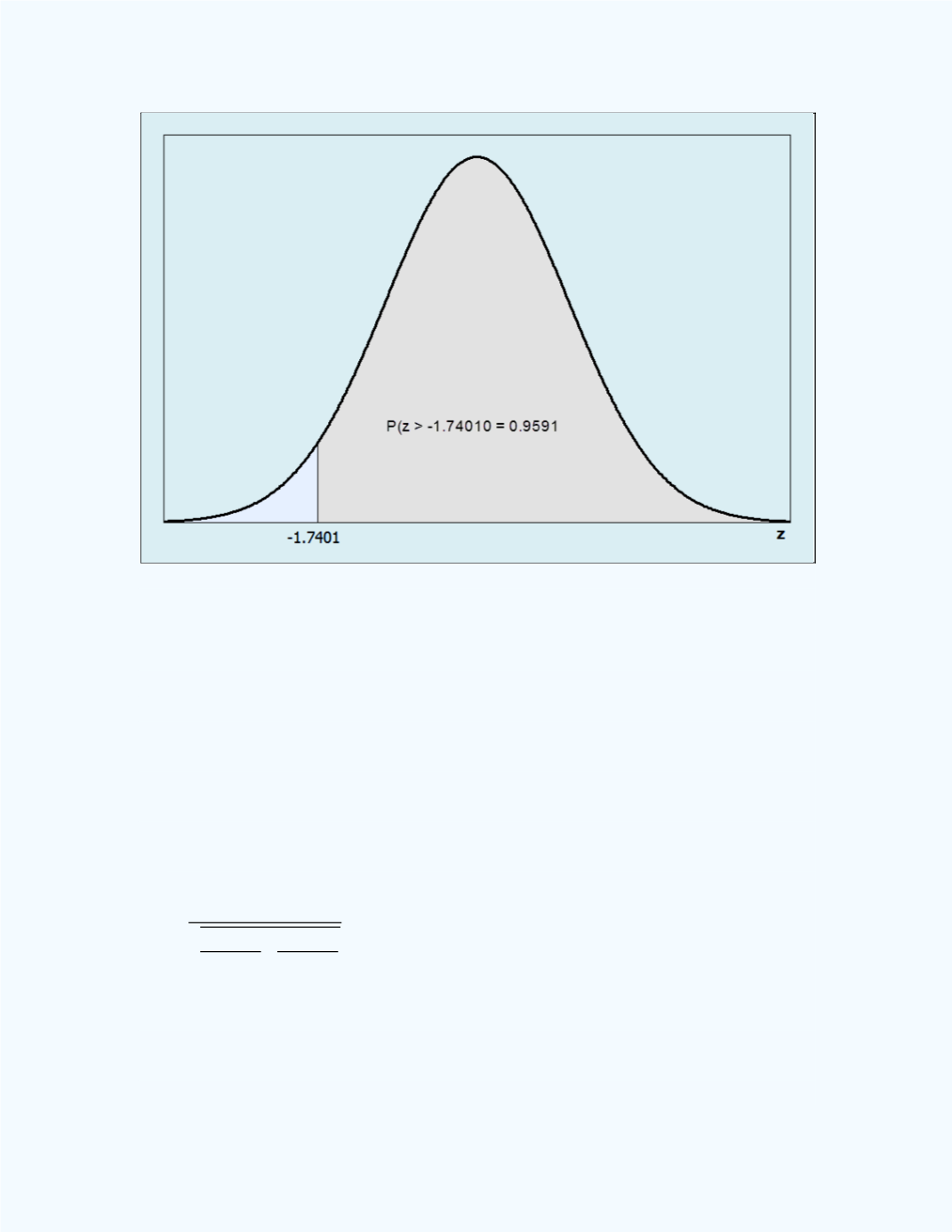
Figure 10-25:
Area for
P
(
̂
1
-
̂
2
0.10) =
P
(z > -1.7401) in
Example 10-5
Example 10-6:
For the data given in
Example 10-5
, what is the
probability that the difference in the proportion of success fromUniversity 1
and University 2 will lie between 0.1 and 0.4?
Solution
: From
Example 10-5
, the assumptions for the Normality
approximation were verified. Thus we can proceed to invoke the
Central
Limit Theorem for the Difference betweenTwo Sample Proportions
.
We need to determine
P
(
̂
1
-
̂
2
0.4). We can substitute into
(̂
̂
)
√
to compute the corresponding z-scores. For the left
hand value of 0.1,
z
= -1.7401 and for the right hand value of 0.4, z = +
1.7401. Thus
P
(
̂
1
-
̂
2
0.4) =
P
(-1.7401
1.7401) = 0.9182
obtained from the
Normal Probability Distribution
workbook shown in
Figure 10-26
.
















