
Chapter 5: Bivariate Data
193
Note:
This is only one way to compute the value of the linear correlation
coefficient proposed by the statistician Karl Pearson. It was presented
because of the simplicity of the computations required for the formula.
There are several other ways to find the value of
r
which will not be
discussed.
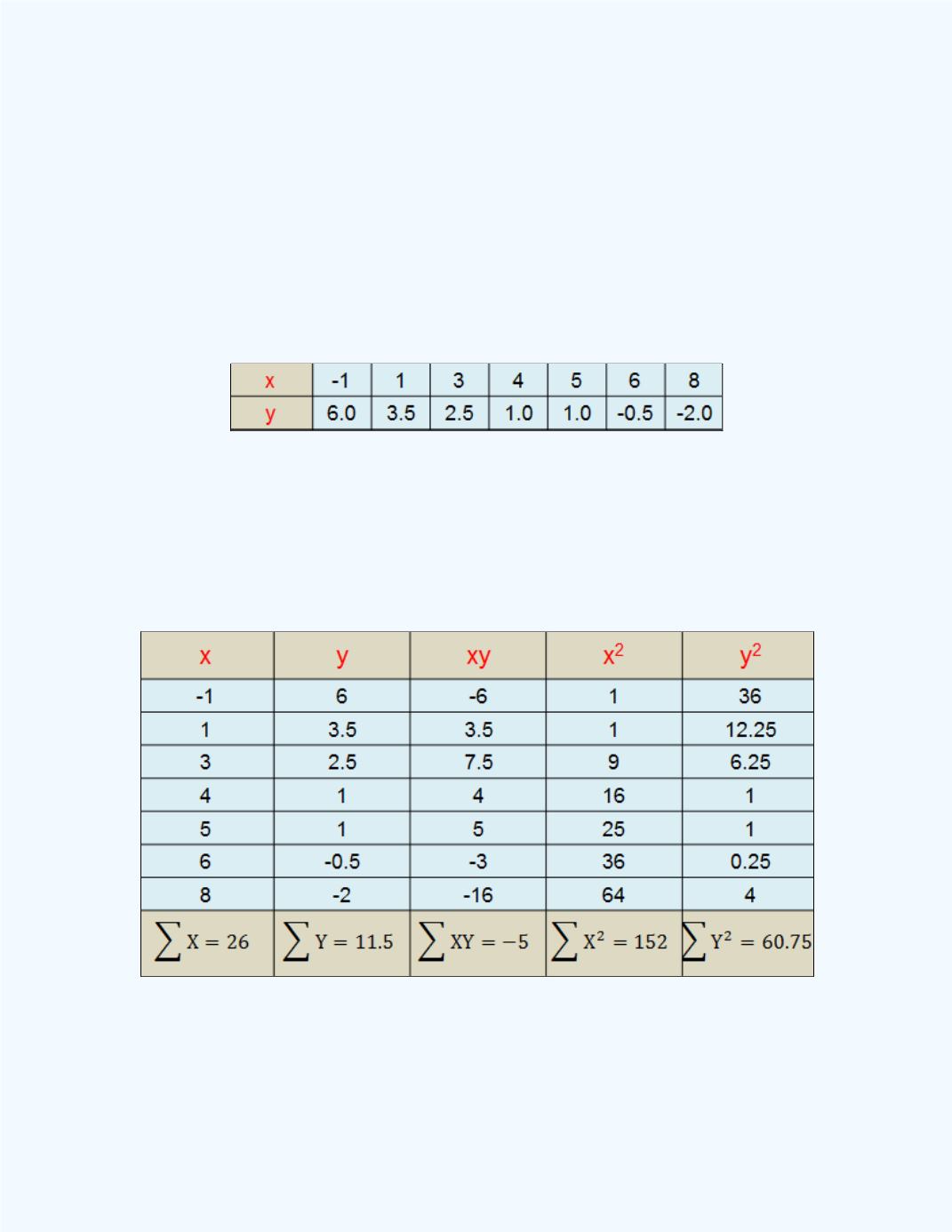
Example 5-2:
Compute the correlation coefficient for the following set of
sample observations for the independent variable (
x
) and the dependent
variable (
y
).
Solution:
The formula may look intimidating, but we can construct a table,
as shown in
Table 5-1
,
to help with the computations. We can use a table
such as
Table 5-1
to obtain the different sums in the formula.
Table 5-1:
Table to help with the Computation of
r
Using the values from
Table 5-1,
we can substitute into the formula and do
the computations. The result is shown next.
















